Generative AI in Insurance: Use Cases, Potential Benefits, and Risks
The (Generative) Elephant in the Room – Are We in an AI Bubble?
ChatGPT launched on November 20, 2022, and was the fastest product to reach 100 million users in history, doing so in just under two months. Nearly a year later, the hype surrounding ChatGPT, and Generative AI more broadly has only accelerated. Nearly every industry imaginable is scrambling to explore, invest in, and understand the potential ramifications of this groundbreaking technology. Supported by billions of dollars in funding, the pace of innovation is staggering. Just last week, OpenAI announced the ability to create custom-GPT’s, which could be its App Store moment and spur an even greater rise in popularity akin to the early days of the iPhone.
The question is – are we in a GenAI bubble? While exploring Generative AI’s potential is (likely) akin to exploring how to use the internet for your business in the late 90s or early 2000s, are we going to see a similar bubble pop? The future is still being written, but our position is that carriers need to continue to focus on core problems such as reducing premium leakage and nondisclosure while exploring future applications of GenAI.
A Brief History of Generative AI
In this article, we will discuss the potential use cases for Generative AI in insurance. But first, let’s take a quick look at where this recent phenomenon came from. Generative AI, a subset of artificial intelligence, has recently exploded in popularity due to the virality of ChatGPT. It has shown incredible potential in various industries and is the fastest app to ever reach 100 million users.
It should be noted, however, that this technology is not brand-new. Instances of Generative AI date back to the 1960s, in the early days of chatbots. In 2014, with the introduction of generative adversarial networks, or GANs, Generative AI took a major leap forward. GANs are a type of machine learning algorithm that enables generative AI to create seemingly authentic images, videos, and audio. Two additional advancements made the recent explosion in popularity possible – transformers and the large language models they enabled.
TechTarget does a great job explaining these advancements. “Transformers are a type of machine learning that made it possible for researchers to train ever-larger models without having to label all of the data in advance. New models could thus be trained on billions of pages of text, resulting in answers with more depth. In addition, transformers unlocked a new notion called attention that enabled models to track the connections between words across pages, chapters, and books rather than just in individual sentences. And not just words: Transformers could also use their ability to track connections to analyze code, proteins, chemicals, and DNA.”
This led to what is better known today as Large Language Models, or LLMs. LLMs are the base of apps like ChatGPT. We’re still in the very early days of building out the app layer and the interfaces we will use in the future. While the generative AI investment bubble continues to inflate, fueling the next generation of applications built for end-users, we wanted to take a look at the potential impact on the insurance industry.
The Promise of Generative AI in Insurance
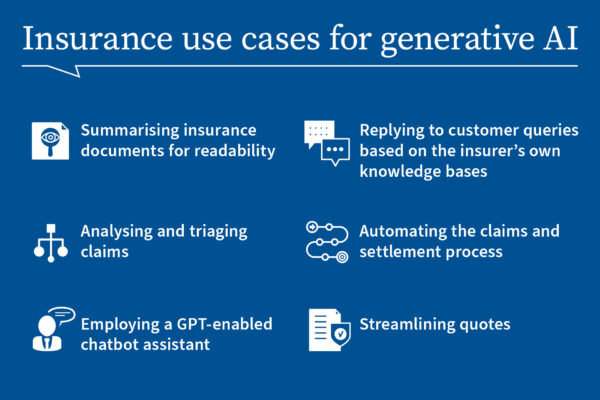
Generative AI has the potential to transform various aspects of the insurance industry, bringing efficiency and an improved customer experience. Here are some examples of how generative AI might be applied:
- Summarizing Insurance Documents:
- Generative AI can be employed to analyze and summarize complex insurance documents, policies, and contracts, such as an Attending Physician Statement (APS).
- By extracting key information and providing concise summaries, it can enhance readability for both customers and internal staff, facilitating quicker decision-making.
- Analyzing and Triaging Claims:
- Generative AI can assist in the initial analysis and triage of insurance claims.
- Automated systems can review claim documents, extract relevant details, and categorize claims based on complexity or urgency, streamlining the claim processing workflow.
- Automated Content Creation:
- Generative AI can potentially streamline the creation of complex insurance documents, policy agreements, and even marketing materials. By analyzing existing data, the technology might be able to generate coherent and tailored content, reducing manual work and improving turnaround times.
- Streamlining Quotes:
- Generative AI can optimize the process of generating insurance quotes.
- By analyzing historical data, market trends, and customer information, it can provide accurate and competitive quotes quickly, improving the efficiency of the underwriting process.
- Automating Claims and Settlement Process:
- Generative AI can play a crucial role in automating parts of the claims and settlement process.
- Automated systems can assess claims against predefined criteria, flagging anomalies or potential fraud. They can also facilitate faster and more accurate settlement calculations.
- Replying to Customer Queries:
- Generative AI-powered chatbots can be integrated into customer service systems.
- These chatbots can provide instant and accurate responses to customer queries by leveraging a vast knowledge base, ensuring consistency and efficiency in customer interactions.
- Generative AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants can provide instant responses to customer inquiries. This allows for 24/7 support and frees up human agents for more complex tasks.
- Enabling GPT Chatbot Assistants:
- GPT-powered chatbots can serve as virtual assistants, guiding customers through various processes, such as policy selection, claim submission, or status tracking.
- They can understand natural language queries and provide personalized assistance, enhancing the overall customer experience.
Can Generative AI be Used in Insurance Underwriting?
The consensus is that yes, it can. We’re a little more skeptical. In Life insurance, machine learning aids risk assessment alongside rules-based engines to remove bias and ensure fairness. Life underwriting is highly regulated and carriers are cautious to use anything black-box that may introduce bias and regulatory scrutiny.
P&C underwriting has a little more leeway, but most data scientists will be quick to tell you that there is an important distinction between machine learning and true artificial intelligence.
-
ML is concerned with making machines learn patterns from the available data so that they can then make predictions on unseen data. ML is a data-driven approach that uses algorithms trained on data to produce models that can perform complex tasks. ML aims to teach a machine how to perform a specific task and provide accurate results by identifying patterns.
- AI is a broad term that refers to systems or machines that mimic human intelligence. AI deals with making machines simulate human cognitive abilities and actions without human assistance. AI can sense, reason, act, and adapt.
While we’re getting closer to AI in some respects, we don’t feel that regulators will allow true AI to be used in underwriting any time soon, if ever.
Despite our feelings, here are some ways we’re hearing that it could potentially help in underwriting:
- Personalized Policies: With the capacity to process large volumes of customer data, generative AI might be able to create highly customized insurance policies that cater to individual needs. This level of personalization enhances customer satisfaction and engagement.
- Risk Modeling and Scenario Planning: Generative AI can simulate numerous scenarios based on historical and real-time data, assisting insurers in developing more accurate risk models. This allows for proactive adjustments to underwriting strategies, enabling insurers to stay ahead of emerging risks.
- Fraud Detection and Prevention: By analyzing patterns and detecting anomalies in large datasets, generative AI can enhance fraud detection and prevention. This technology can quickly spot irregularities in claims or behavior, helping insurers mitigate financial losses.
- Dynamic Pricing Models: Generative AI can contribute to the development of dynamic pricing models that adjust premiums based on evolving risk factors and market conditions. This flexibility allows insurers to adapt their pricing strategies in real-time, improving competitiveness and profitability.
Why Generative AI Benefits for Insurance Might Take Time
The deployment of generative AI in insurance, while holding the promise of increased efficiency and streamlined processes, is not without its downsides.
One significant concern lies in the potential for mistakes to be compounded, leading to substantial and costly errors. For instance, in tasks such as summarizing an Attending Physician’s Statement (APS), even a minor error can have far-reaching and expensive consequences, resulting in millions in costs. Unlike human errors, which may be more forgivable in the eyes of policyholders and carriers alike, mistakes made by AI systems can face heightened scrutiny. We’re seeing a similar dynamic play out in the autonomous vehicle space. Striking the right balance between automation and human oversight is crucial to mitigating the risks associated with costly errors while leveraging the benefits of advanced technology in insurance operations.
While generative AI remains in vogue, our position is that it will take years for its widespread adoption in insurance, especially underwriting. Here are some other reasons behind the potential delay:
- Data Availability and Quality: Generative AI requires large amounts of high-quality data to generate accurate insights. Many insurers are still in the process of digitizing their data and improving its quality. Additionally, generative AI and LLMs have a long way to go before the application layer is vertically specific.
- Complexity of Underwriting: Insurance underwriting involves intricate decision-making that considers a multitude of factors. Developing generative AI models that accurately replicate this decision-making process is a complex task. Carriers today are still very focused on explainability when dealing with advanced machine learning and often default to rule-based approaches to remain compliant. We struggle to see how carriers will make the leap to black box genAI systems anytime soon.
- Regulatory Challenges: The insurance industry is heavily regulated, and deploying generative AI models will require thorough testing and regulatory approval.
- Complex Implementation: Integrating generative AI into existing insurance workflows can be intricate and resource-intensive. Proper training, data preparation, and system integration are necessary for effective implementation.
- Ethical and Fairness Concerns: Generative AI models must be carefully monitored to ensure they don’t inadvertently introduce biases or unfair practices into the underwriting process.
Our Suggestion
While exploring the potential of generative AI is worthwhile, we believe carriers should maintain a balanced approach. In the near term, the focus should remain on addressing pressing issues such as reducing premium leakage and nondisclosure and growing gross premiums to ensure immediate and tangible improvements in profitability and efficiency.
At the same time, it is crucial to allocate sufficient resources and energy toward understanding and experimenting with generative AI. By doing so, carriers can stay ahead of technological advancements and be well-prepared to integrate these innovations when they mature.
At ForMotiv, we’re always keeping an eye on emerging technologies to see if they would be beneficial for us or our customers in the future. We see ML and AI reinventing Vertical SaaS companies. The emerging Vertical SaaS companies can drive hyper-personalization, better risk management, and deter old and new kinds of fraud. In insurance, we see AI continuing to disrupt the insurance market by automating middle and back-office manual tasks. In fact, that is just getting started.
This will result in faster and more accurate underwriting and claims processing. We think this trend is a great tailwind for us as more and more aspects of insurance go digital and require real-time triage decisions. Our proprietary dataset and algorithms put us in a unique position to benefit from carriers using more AI as it can’t be replicated elsewhere.
Striking this balance will enable carriers to benefit from current solutions that offer immediate impact, such as leveraging ForMotiv’s capabilities to enhance Placement and Bind Rates while minimizing risks with Nondisclosure and Leakage Solutions. Simultaneously, investing in generative AI research and pilot programs will position insurers to capitalize on future advancements, ensuring they remain competitive and innovative in the long run.
Reach out to learn how some of the biggest carriers in the US are effectively balancing their near-term focus with future-oriented AI exploration.